NANOTECHNOLOGY
Nanoparticles - The Basics
At the nanoscale, typically defined as the size range between 1 and 100 nanometers (nm), physical forces are overtaken by chemical and molecular laws that govern how particles interact. Nanotechnology is not simply working at ever smaller dimensions; rather, working at the nanoscale enables us to utilize the unique physical, chemical, mechanical and optical properties of materials that do not naturally occur at the macroscopic size scale.
0
RICHARD FEYNMAN INTRODUCED NANOTECHNOLOGY
0
x
SMALLER THAN A GRAIN OF SAND
0
nm
WIDTH OF HUMAN HAIR



NANOPARTICLE
10-9 m


SOCCER BALL
10-1 m

EARTH
106 m
Nanotechnology Explained
Nanotechnology deals with materials at the extreme side of scale — between 1 and 100 nm. At the nanoscale, there are more atoms located on the outside of the particle that are available to interact with other species relative to atoms contained within the bulk of the particle, expressed as a Specific Surface Area (SSA). This gives rise to unique physical, chemical, mechanical and optical properties of nanomaterials that do not naturally occur at the macroscopic size scale. Our nCore™ platform technology can produce nanoparticles as small as 3 nm in bulk industrial quantities. Click below to learn more.
SPECIFIC SURFACE AREA VS SIZE
NANO
MICRO
MACRO
0
m2/g
m2/g
9
m2/g
nanoscale - size matters
Nano-scale objects exhibit unique properties that are not commonly found in their larger counterparts. This unlocks a whole range of applications previously thought impossible. It is important to understand how chemical and physical characteristics of materials are a function of their size. See below to learn more.
NANOPARTICLE
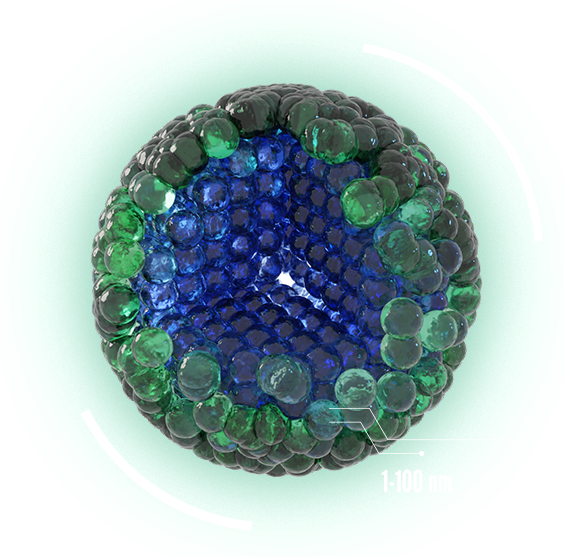

At the nano-scale, the ratio of
outer to inner atoms is relatively high, meaning they are readily available to interact with other surrounding atoms. This results in a very high specific surface area and surface activity. The number of particles per unit volume is also high.
SURFACE AREA
SURFACE ACTIVITY
PARTICLES PER UNIT VOLUME
MICROPARTICLE
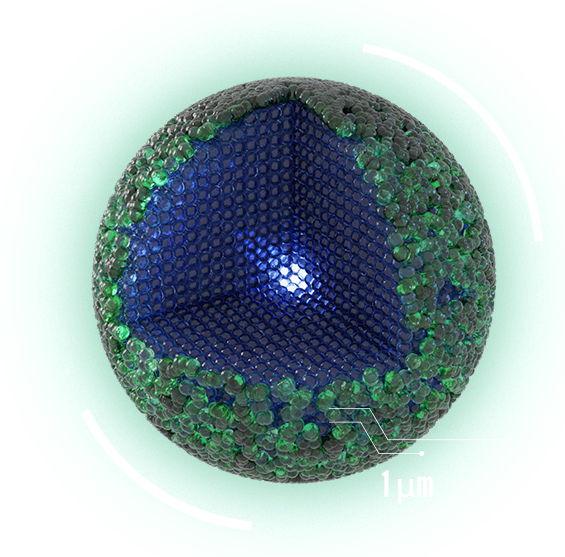

Micron-sized particles have much lower specific surface area and surface activity because majority of atoms making up the particle are 'locked' inside. There are fewer particles per unit volume.
SURFACE AREA
SURFACE ACTIVITY
PARTICLES PER UNIT VOLUME
MACROPARTICLE
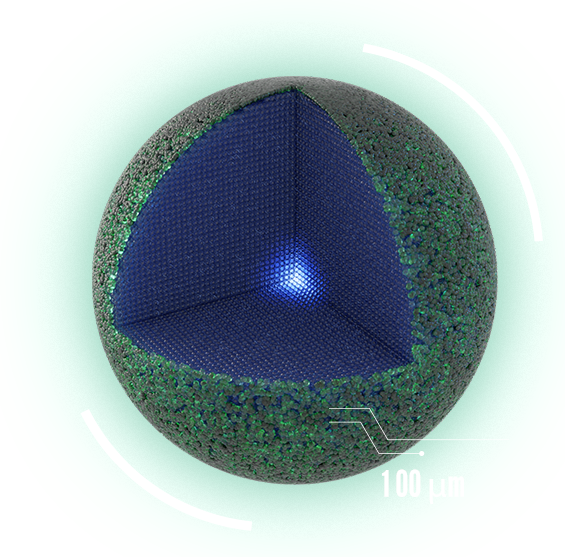

Everyday-sized, macroscopic objects have such low specific surface area and surface activity, that those forces become negligible. There are very few particles per unit volume.
SURFACE AREA
SURFACE ACTIVITY
PARTICLES PER UNIT VOLUME
Play Video
CONTACT US
nFluids Inc.
253147 Bearspaw Rd
Calgary, Alberta, Canada
T3L 2P5
Mon – Fri | 9:00 – 17:00 MT
Weekend | Holidays – May vary
Business Development | Investor Relations :
Business Operations | Research & Development :
Hai Wang
Phone Number: 587.892.3631
E-mail: [email protected]
